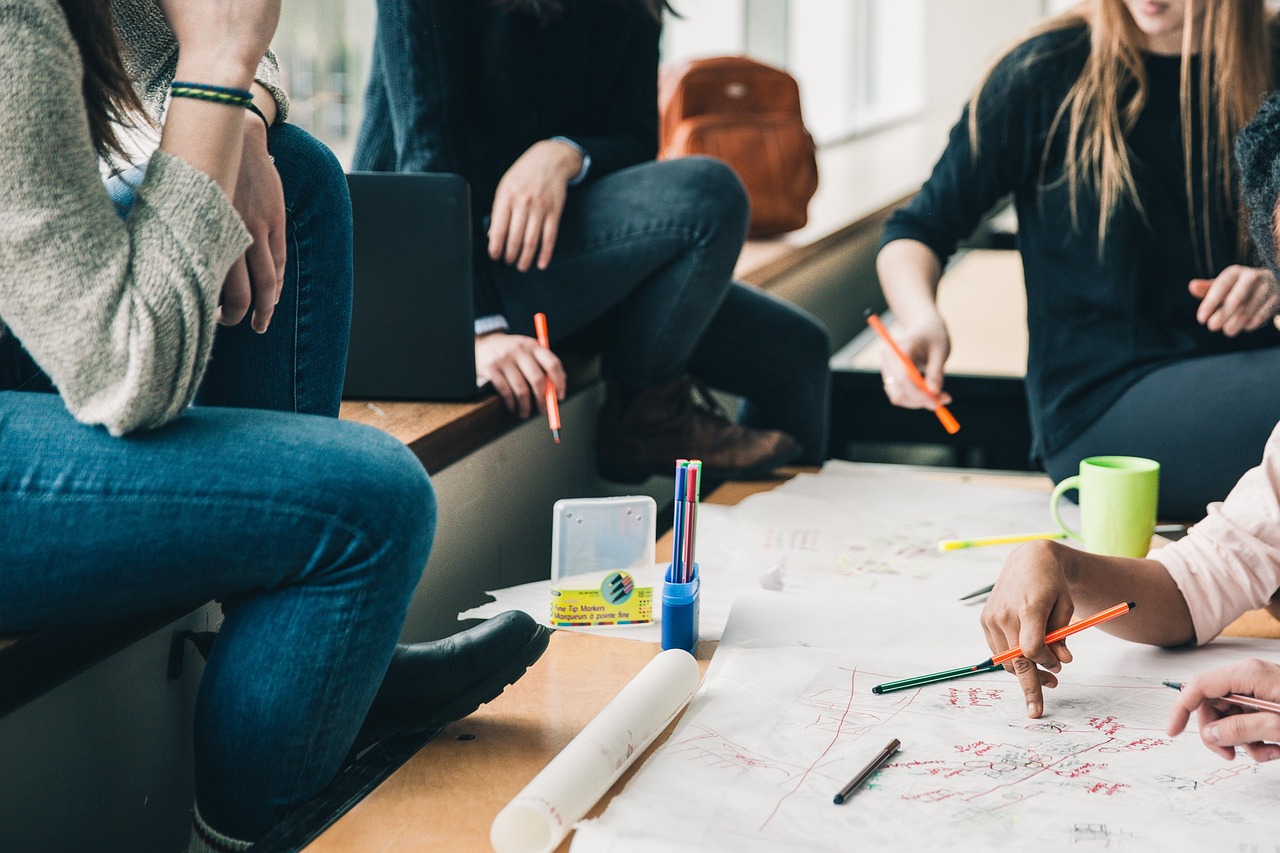
Immigration to the United States can be a long and stressful journey, but it doesn’t have to be a solo journey. With the help of a sponsor, immigrants can receive the support they need to transition into their new life and give United States immigration officials confidence that they will succeed in the country. For some immigration avenues, sponsorship is mandatory. If you or your family members are currently deciding the best immigration path forward, learning what sponsorship entails can help you decide what to pursue.
What Are Immigration Sponsors?
An immigration sponsor is an individual or entity that agrees to take financial and legal responsibility for an immigrant entering the United States. The sponsor typically files an Affidavit of Support (Form I-864) or Petition for Alien Relative (Form I-130) with U.S. Citizenship and Immigration Services, legally binding documents with serious, long-term responsibilities. At the most basic level, the U.S. government wants to ensure that the immigrants will not become a public charge, meaning they won’t rely on public benefits like welfare.
Sponsorship is required for every person who immigrates based on a relative petition. If a family member is sponsoring a relative, they don’t necessarily have to provide financial support; they can find others willing to take on this commitment by filing affidavits of support.
Who Can Sponsor an Immigrant?
Not everyone can sponsor an immigrant; there are specific requirements and qualifications. In general, sponsorship is possible if the sponsor has a relevant interest in the immigrant and is willing to take on added responsibilities to ensure they benefit the country. The most common sponsors include:
- U.S. Citizens and Lawful Permanent Residents: Family members, such as spouses, parents, children, and siblings, can sponsor their relatives and help them pursue permanent residency.
- Employers: Companies can sponsor foreign workers for employment-based visas, provided they have an approved petition.
- Certain Organizations or Groups: Organizations can sponsor individuals in specific cases, especially under humanitarian or religious visas.
To qualify as a sponsor, someone must:
- Be at least 18 years old.
- Reside in the United States.
- Demonstrate a clear ability to support the immigrant financially as they enter and live in the U.S., typically by proving an income at least 125% of the federal poverty level.
Some of these requirements are flexible in certain circumstances. For example, active duty military financial requirements are lower when sponsoring immediate family members. In addition, assets, in conjunction with income, are sometimes allowed in financial calculations.
What happens if the sponsor can no longer meet the financial requirements?
If a sponsor’s financial situation changes due to job loss, unexpected expenses, or other factors, they may struggle to maintain the required support. Unfortunately, this can delay the immigration process or even jeopardize the immigrant’s status. In some cases, additional sponsors may step in, which adds even more complexity and wait time.
How long is a sponsor held legally responsible for the immigrant?
By signing an Affidavit of Support, sponsors agree to support the immigrant until one of several conditions is met:
- the immigrant becomes a U.S. citizen,
- the immigrant has worked 40 qualifying quarters
- the immigrant permanently leaves the United States.
Sponsorship can be a long-term commitment, and sponsors should fully understand the timeline and legal responsibilities before agreeing to sponsor someone.
Even with all this info, deciding whether sponsorship is right for you can be a challenge. Luckily, when you work with experienced Florida immigration attorneys, we leverage our experience and apply it to your situation to find the best path forward. Contact Probinsky & Cole today to speak to our team and learn how we can help you and your family with immigration challenges.