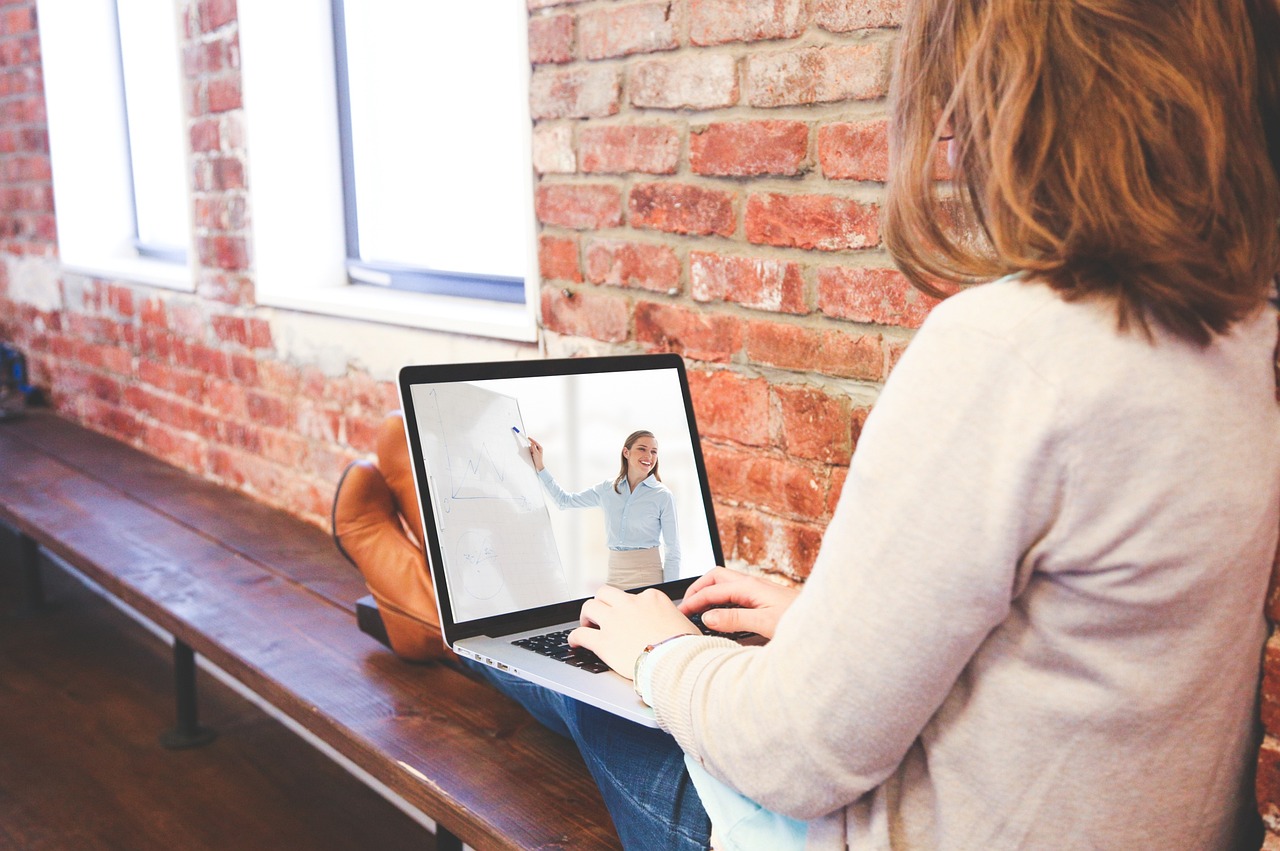
Remote work has become a permanent fixture in today’s professional landscape, reshaping how businesses operate and how employees manage their daily lives. While working from home offers flexibility and cost-saving benefits, it also introduces a wide range of legal considerations that both employers and employees must understand. From tax implications to data security, navigating the legal side of remote work is essential for maintaining a productive and secure work environment.
Employment Law Compliance
One of the most important legal implications regarding remote work revolves around employment law compliance, particularly when employees work from regions different from the employer’s primary location. Labor laws vary by jurisdiction, and employers are generally required to follow the laws of the employee’s work location, not just the company’s headquarters.
This means complying with local wage and hour laws, mandatory rest breaks, overtime rules, and paid leave regulations. For example, if a Florida-based employer has a remote employee working from California, that employee is entitled to California’s more stringent labor protections. Employers must also ensure they follow state-specific rules for non-compete clauses, termination procedures, and anti-discrimination laws.
To stay compliant, businesses should consider creating a remote work policy that addresses:
- Where employees can work from
- How hours are tracked
- What legal jurisdictions the company is willing to operate under
Consulting legal counsel to review multi-state compliance issues is highly recommended for businesses with a remote workforce spread across different regions.
Tax Implications of Remote Work
Remote work also raises questions about state and local tax obligations. Employees working in a state different from their employer may trigger tax nexus for the company, potentially requiring the business to register, file, and pay taxes in that state. This can be particularly complex if the employee resides in a state with income tax, while the employer is based in a tax-free state like Florida.
From the employee’s perspective, working remotely may mean being subject to different income tax filing requirements. Some states have reciprocal agreements to avoid double taxation, while others may not, leading to potential confusion and higher tax burdens.
Employers should also understand the rules around payroll tax withholding and determine whether they need to adjust how and where taxes are collected for their remote employees. It’s crucial to consult with a tax advisor to ensure compliance and avoid penalties.
Remote Work: Data Security and Privacy
When employees work remotely, particularly from home or public spaces, data security becomes a top legal and operational concern. Employers are responsible for safeguarding sensitive company and client information, regardless of where employees access it. This includes complying with privacy regulations such as HIPAA or state-specific data protection laws like the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA).
Remote work environments can increase the risk of data breaches due to unsecured Wi-Fi networks, shared devices, or weak password practices. Employers must take proactive steps to minimize these risks by providing:
- Encrypted devices and secure software
- Virtual private network (VPN) access
- Mandatory cybersecurity training
- Clear policies for handling sensitive information
Employers should also have remote work agreements in place that outline the employee’s responsibilities regarding data protection and the use of company-owned technology.
Workers’ Compensation and Workplace Safety
Another often overlooked legal issue is workers’ compensation liability. Remote employees are still eligible for workers’ compensation if they are injured in the course of performing their job duties—even if that happens at home. Employers need to consider how to evaluate and document remote workspaces and address workplace safety standards for employees outside of the office.
Creating a process for reporting injuries and conducting virtual safety assessments can help reduce liability while ensuring employees stay safe.
As remote work evolves, businesses that proactively address these legal implications will be better positioned to thrive in the modern workplace. Call a professional attorney well-versed in workers’ compensation law if you’re navigating remote work policies and legal risks.
Probinsky & Cole has offices in Sarasota, Brandon (Tampa), and Orlando.